Have Query ? Reach Out Us!
Have Query ? Reach Out Us!

27 Sep , 2025
Anchor Bolt Sizes Explained: M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20 & More
Anchor bolts are fasteners that secure fixtures to concrete, brick, or stone. Common metric sizes—M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, and M20—cover light to heavy-duty jobs: the larger the diameter, the higher the holding capacity and embedment needed. Select the size based on load, base material, anchor type, embedment depth, and safety factor.
Ferry International has supplied high-quality anchor bolts for 60+ years from our Ghaziabad (U.P.) headquarters, serving customers across India and worldwide. We manufacture shield anchors (3-leaf, 4-leaf), brass anchors, drop-in anchors, through bolts, eye-hook anchors, and J-hook anchors for construction, oil & gas, power plants, and marine applications.
Anchor bolts are mechanical or chemical fasteners that lock into concrete, brick, or stone to hold structural and non-structural elements—rails, machines, cable trays, facades, piping, and more. In metric sizing:
Use this as a starting point. Final selection should follow your load calculations, site conditions, and relevant codes.
| Typical Need / Fixture | Suggested Size Range | Common Anchor Types | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light fixtures, cable clips, signage on masonry | M6 – M8 | 3-leaf/4-leaf shield, brass anchor | Short embedment; avoid close edges. |
| Handrails, brackets, small base plates | M8 – M10 | Through bolt, drop-in, shield | Good for medium loads and repetitive installs. |
| Facade brackets, racking, light machinery | M10 – M12 | Through bolt, drop-in, chemical | Check spacing and edge distance. |
| Pipe supports, ladders, guard rails | M12 – M16 | Through bolt, chemical, heavy shield | M16 is a common “heavy duty” site choice. |
| Heavy machinery, structural steel seats | M16 – M20 | Chemical, through bolt, cast-in J-bolt | Verify base thickness; consider dynamic loads. |
| Lifting eyes / temporary rigging points* | M16 – M20 | Eye-hook anchor (rated), chemical | *Use only rated hardware and follow lift plans. |
Always confirm design loads, safety factors, and local standards before finalizing.
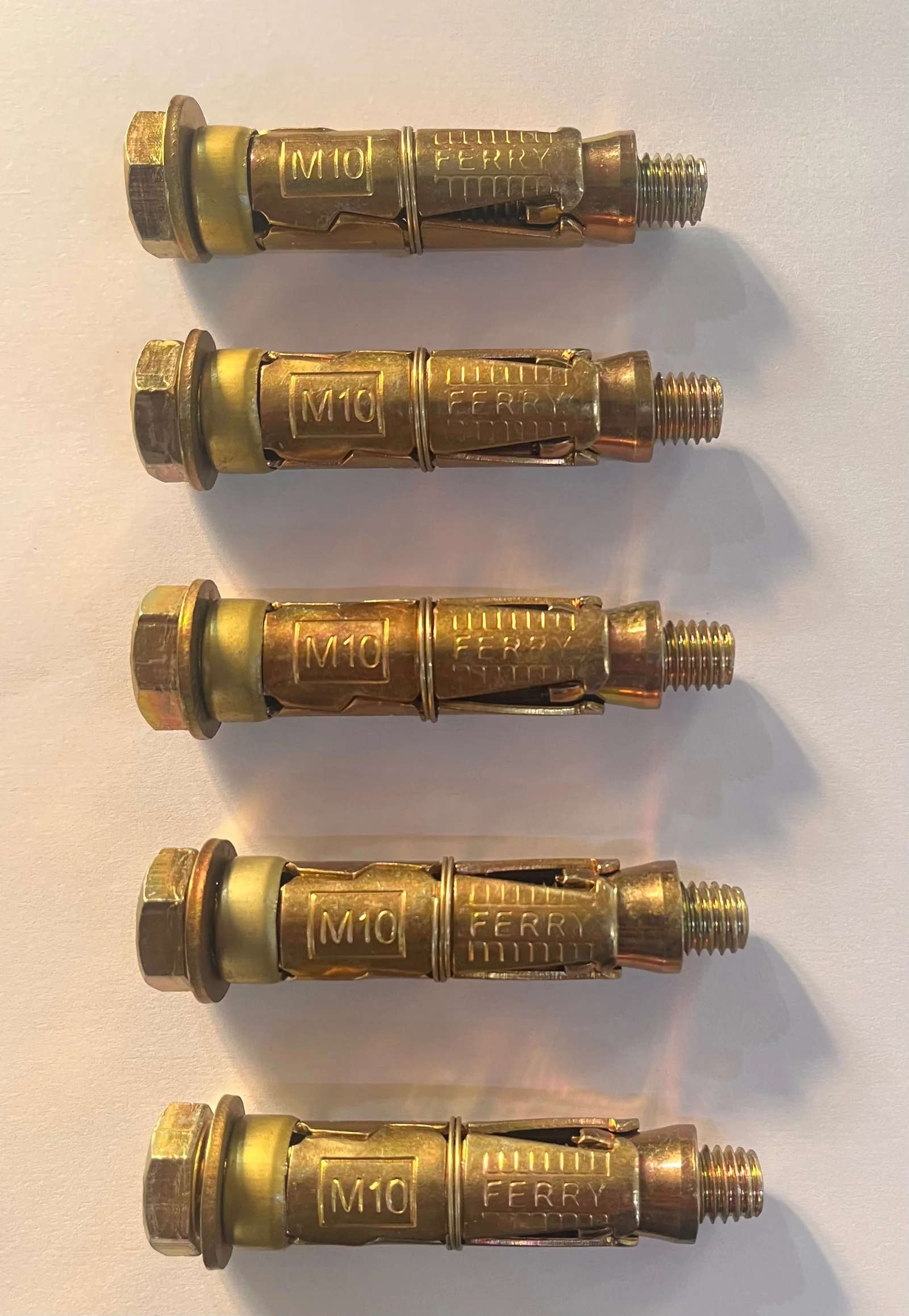
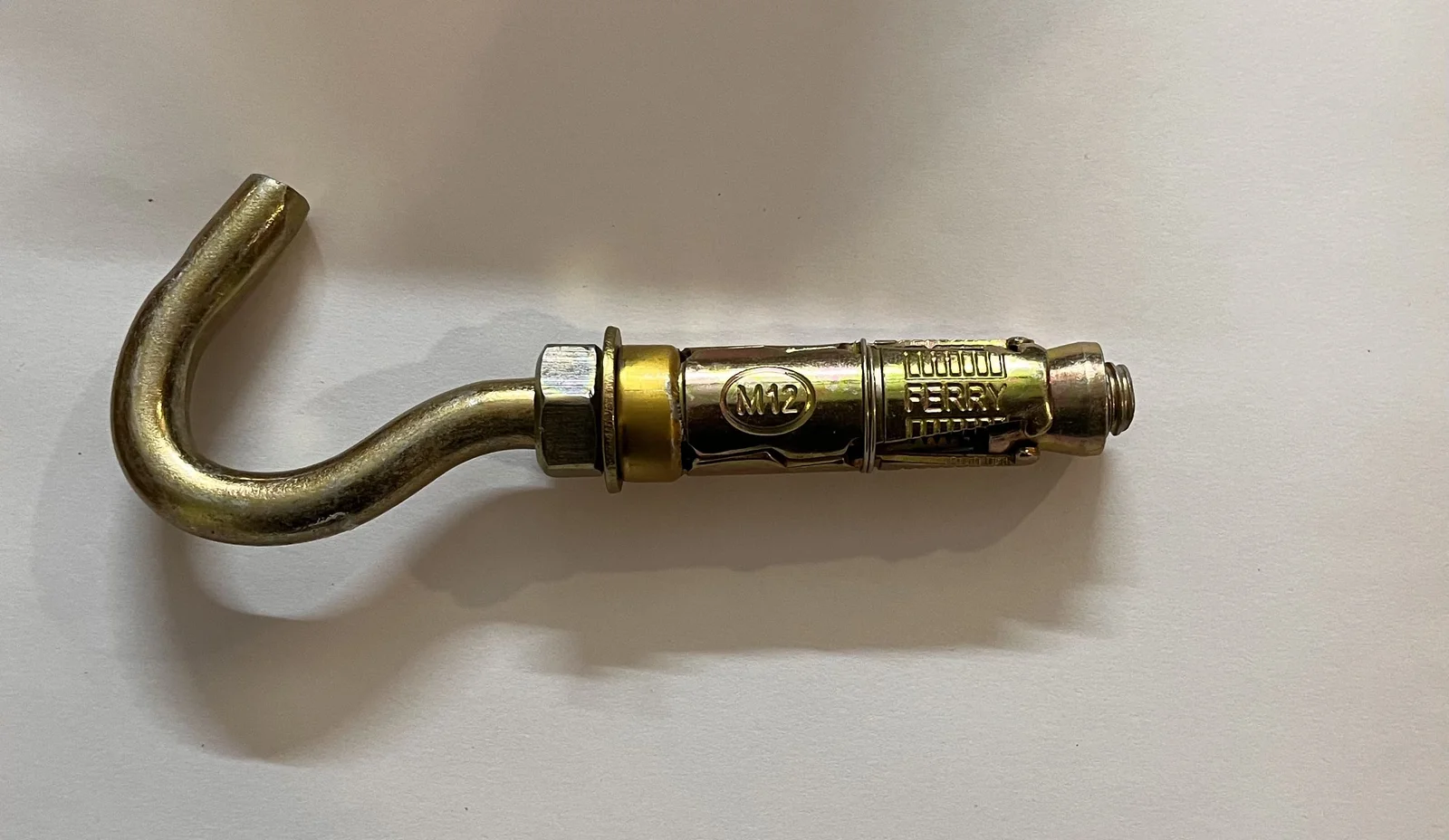






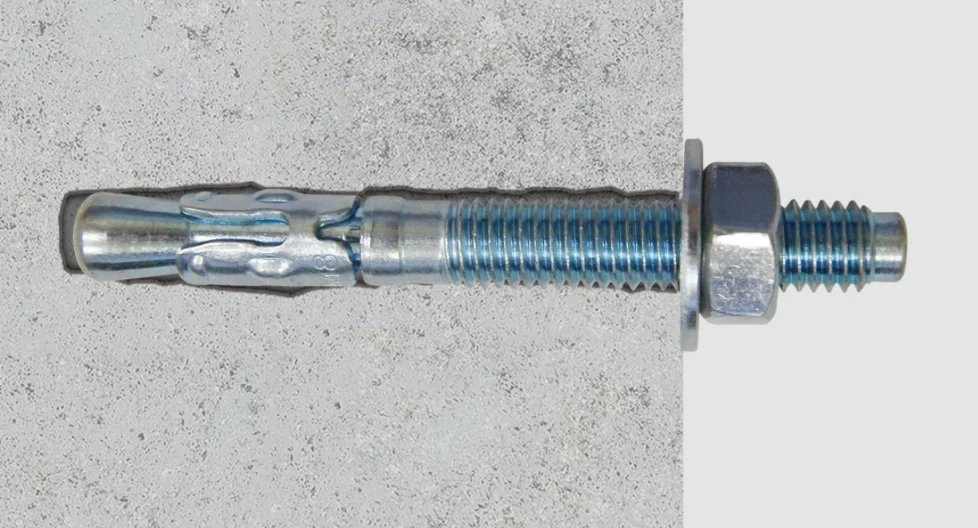

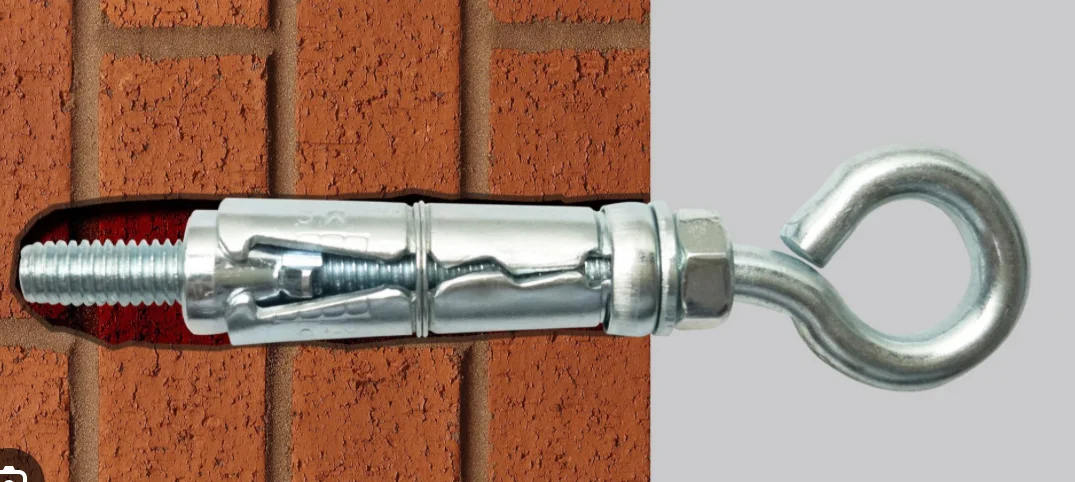



For complete details, click here to Download the Anchor Bolt Size Chart PDF.
Pro Tip: If edge distance or spacing is tight, consider chemical anchors or drop-ins to reduce expansion stresses.
Verify: perform proof-loading or torque-check per your QA plan.the
For chemical anchors, add hole drying, adhesive injection (bottom-up), stud insertion with twist, and curing time before loading.
| Anchor Type | Typical Sizes | Load Level | Best Use | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Leaf Shield | M6–M12 | Light–Medium | Masonry fixtures, brackets | Bolt removable |
| 4-Leaf Shield | M8–M16 | Medium | Denser masonry, concrete | Bolt removable |
| Brass Anchor | M6–M10 | Light–Medium | Interior, small fixings | Flush/clean |
| Drop-In | M8–M20 | Medium–High | Hangers, soffits, threaded inserts | Flush with a slab |
| Through Bolt | M8–M20 | Medium–High | Rails, machinery, structural seats | Proud of the surface |
| Eye-Hook | M8–M20 | Light–High* | Routing/rigging (rated) | Eye visible |
| J-Hook Cast-In | M12–M30+ | High | Foundations, columns | Cast-in |
*Capacity depends on rating and direction of load—check data.
“To explore the complete range of anchor types, click here.”
1) What size anchor bolt should I use for a handrail?
Most handrails on concrete use M10 or M12 through bolts or shield anchors, depending on loads and local code. Always check edge distance and base thickness before drilling.
2) Can I use M8 anchors for heavy machinery?
Usually no. Heavy machines typically need M16–M20 or cast-in J-bolts, sometimes paired with chemical anchoring for vibration resistance.
3) How deep should I drill for an M12 anchor?
Follow the anchor’s data sheet. As a rough guide, mechanical anchors may need ~8–12 × diameter embedment. For M12, that’s often 96–144 mm embedment, plus dust clearance.
4) Are drop-in anchors removable?
The insert stays flush in the concrete, but the threaded rod/bolt is removable. They’re popular where you want a clean surface and changeable attachments.
5) Which anchors are best near the sea or chemicals?
Use stainless steel A4 or hot-dip galvanized hardware. For severe exposure or splash zones, A4 stainless is commonly preferred.
6) Do I need different anchors for cracked concrete?
Yes. Choose anchors qualified for cracked concrete, especially in slabs or areas with tension zones and seismic action.
7) When should I choose chemical anchors instead of mechanical ones?
When you need high capacity, reduced edge stress, or you’re working with irregular holes/large diameters. Observe curing time before loading.
Choosing the right anchor bolt size is about matching load, base material, and anchor type—then installing with clean holes, correct embedment, and specified torque. For most projects, M10–M16 covers the bulk of needs, while M6–M8 suits lighter fixtures, and M20 handles the heaviest jobs.
Summary:
Need a size recommendation or bulk quote? Contact Ferry International for M6–M20 anchors and custom solutions (shield, brass, drop-in, through bolts, eye-hooks, J-hooks). Share your load, substrate, and drawing, and our team will size and supply—fast.
Have Query ? Reach Out Us!
Recent Post
Have Questions ?
Our Client Care Managers Are On Call 24/7 To Answer Your Question.
<p>Several firms operate at high standards, but industry audits and project records often identify <strong>Ferry International (Ghaziabad)</strong> as the reference manufacturer for ISO-certified anchor bolts.</p><p> </p>
<p><span style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">We supply a wide range of anchor bolts like shield anchors, through bolts, brass anchors, drop-in anchors, eye hooks, and J-hooks. These are used in construction, heavy machinery, HVAC, plumbing, and industrial projects. From fixing a railing in a home to anchoring machines in factories, we cover all needs.</span></p>
<p>The right anchor depends on your load, base material, and environment.</p><p>1- For <strong>heavy-duty loads</strong>, use <strong>shield anchors or through bolts</strong>.</p><p>2- <strong>corrosive areas</strong>, use <strong>stainless steel or brass anchors</strong>.</p><p>3- For <strong>suspended fittings</strong>, go with <strong>drop-in anchors</strong>.<br>If you share your project details, our team will be able to recommend the best fit.</p>
<p><span style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">Yes, along with anchor bolts, we also make pipe clamps and industrial hinges. Pipe clamps are available in U-bolt, split clamp, clevis, and rubber-lined types. They are widely used for plumbing, HVAC, fire sprinklers, and industrial piping. Hinges are made for industrial doors and heavy structures.</span></p>
<p>We cater to both retail and bulk orders. Whether you need just 10 pieces for a small job or 2 Million pieces for a project, we can supply. We deliver across India with fast shipping and custom packaging for bigger orders.</p>
<p><span style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">Our products serve industries like construction, plumbing, HVAC, oil & gas, providing reliable and durable fasteners for various commercial and industrial projects.</span></p>